Research · 14 min read
Multimodal Research - Synchronous Recording of Audio, Video & Physiological Data
Comprehensive guide to multimodal research methods, covering synchronized data collection, human factors research, and usability studies using advanced lab solutions.

What is Multimodal Research?
Multimodal research is a scientific approach that combines different methods and types of data to gain broader and deeper insights into complex phenomena. This research approach utilises multiple modalities, which means that different types of data and methods are integrated to illuminate a research topic from different perspectives.
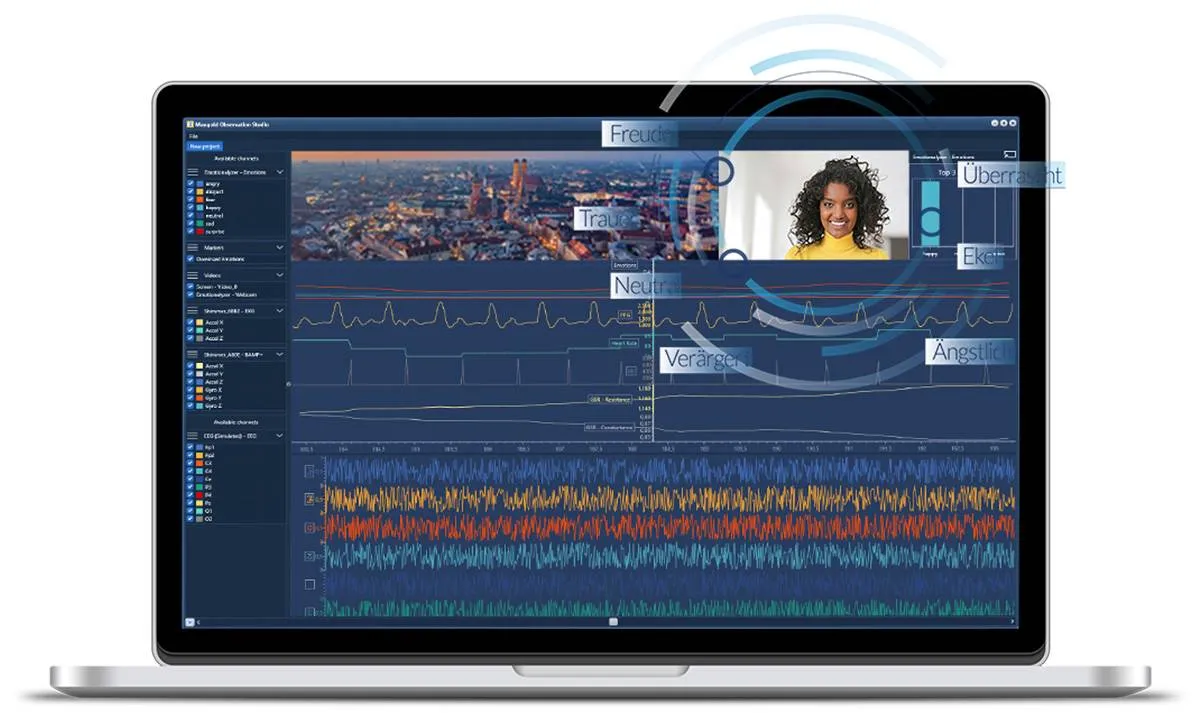
By collecting and integrating these different data sources, both conscious and unconscious reactions can be better understood.
Integration of Different Data Types
- Quantitative data: Number-based data that can be statistically analyzed
- Qualitative data: Descriptive data available as text, images or videos that is analyzed descriptively
Use of Different Research Methods
- Experimental methods: Controlled experiments to investigate causal relationships
- Observation methods: Direct observation of behavior and interactions in natural environments
- Survey methods: Surveys, interviews and questionnaires to gather opinions and experiences
Integration of Different Disciplines
Multimodal research is often interdisciplinary and combines findings from different scientific fields such as psychology, sociology, computer science, neuroscience, and others. Typical application areas are:
- Human Factors research
- Usability and UX research
- Gaming research
- Market research
- Ergonomics
- Neuromarketing
- and more…
Advantages of Multimodal Research
- Holistic understanding: By combining different data sources and methods, researchers can develop a more comprehensive and nuanced understanding of complex phenomena
- Increased validity: Using multiple methods and data sources increases the validity of research results by combining strengths of individual approaches
- Broader perspectives: Multimodal research enables examining issues from different scientific perspectives to gain new insights
Examples of Multimodal Research

- Educational research: Analysis of student performance combining standardized test results (quantitative) and interviews with teachers and students (qualitative) for comprehensive picture of educational quality
- Medical research: Investigation of disease progression combining genetic data, clinical test results and patient interviews
- Cognitive neuroscience: Research into brain processes using combination of imaging techniques (e.g. fMRI, EEG), behavioral studies and psychometric tests
- Technology development: Development and improvement of human-machine interactions through analysis of user data, observation of user interactions and qualitative user feedback
Challenges of Multimodal Research

- Complexity: Integration of different methods and data types requires careful planning and coordination
- Data management: Handling large and heterogeneous data volumes places high demands on processing and analysis
- Interdisciplinary collaboration: Often requires collaboration between researchers from different disciplines, which can pose organizational and communication challenges
All in all, multimodal research is a powerful approach to capturing the complexity of the real world and gaining in-depth, comprehensive insights.
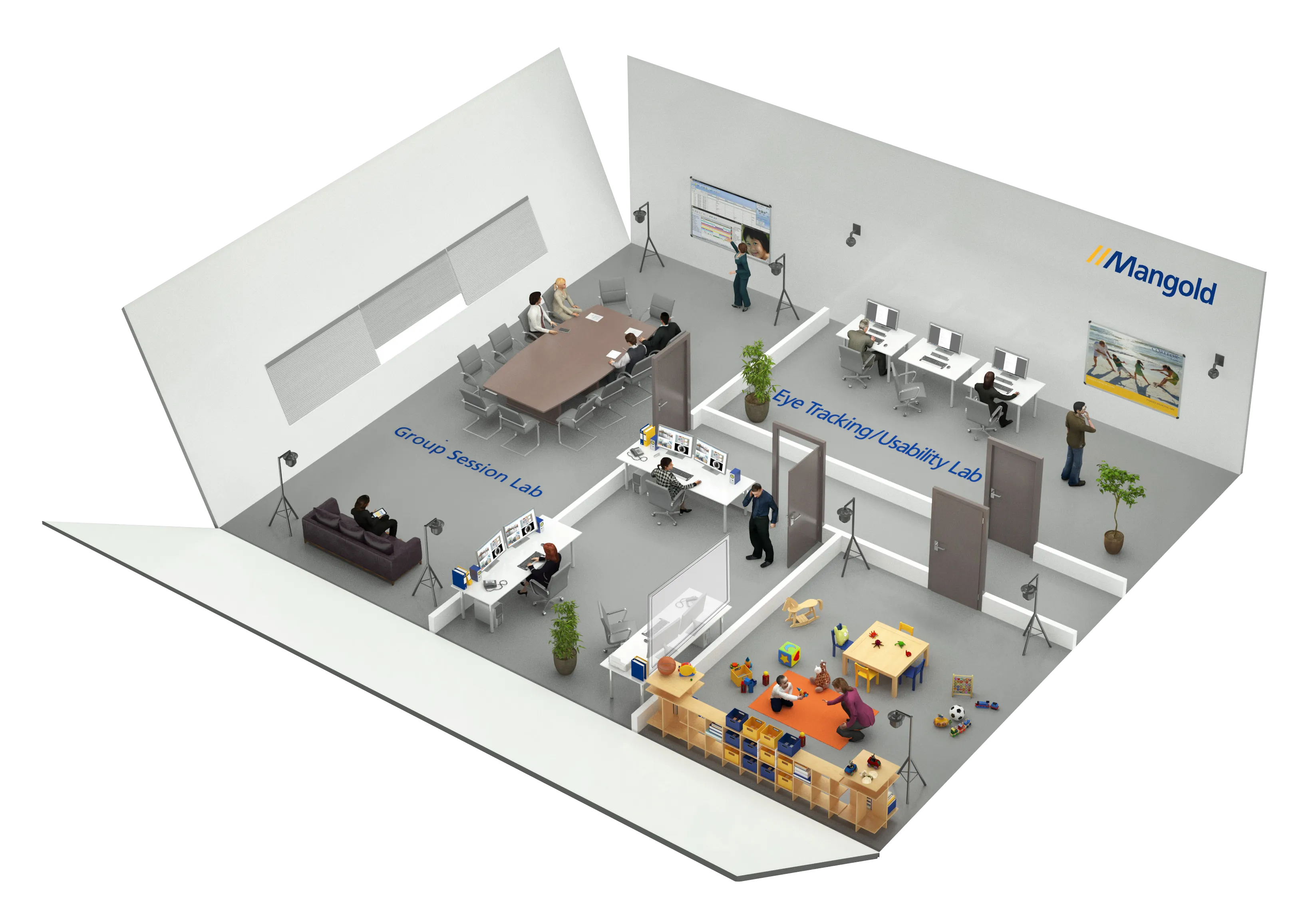
Mangold Observation Studio - The Future of Multimodal Research
Mangold Observation Studio
The advanced software suite for sophisticated sensor data-driven observational studies with comprehensive data collection and analysis capabilities.
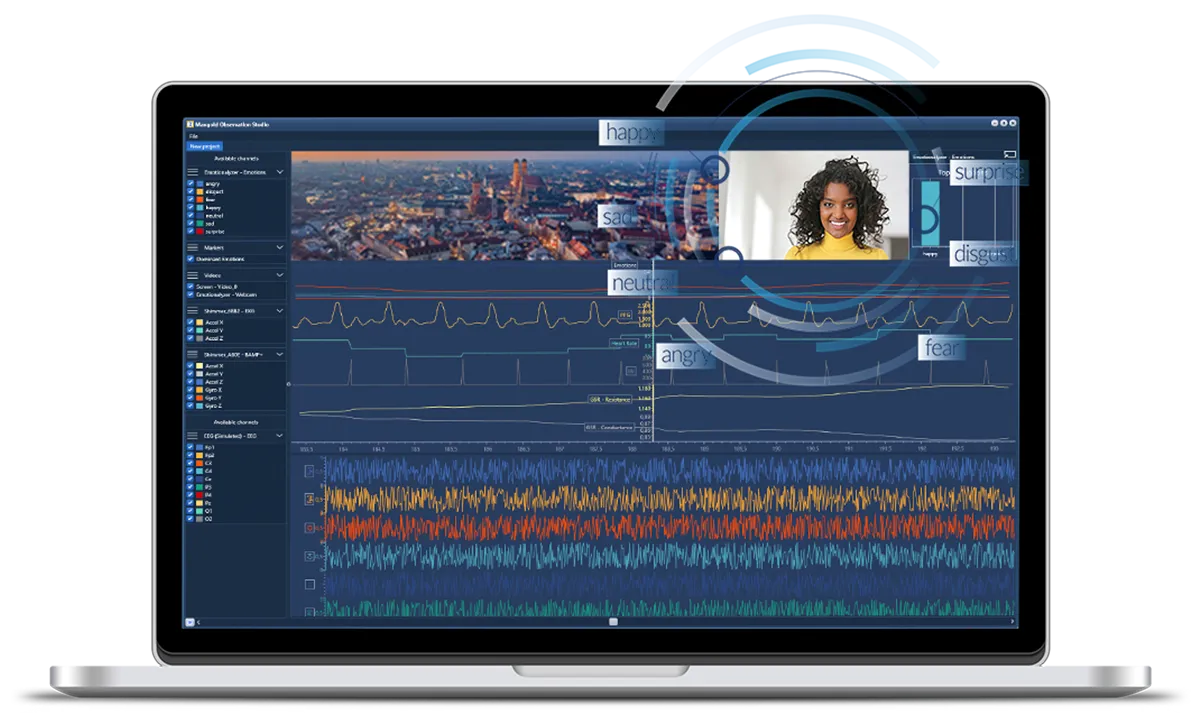
- Record all data synchronously: A core functionality of Mangold Observation Studio is the time-synchronous recording of multimodal data, such as video, physiology, computer screens and more, allowing you to conduct qualitative and quantitative observational studies in a wide variety of applications.
- Easy to use: The system is literally designed as a one-push-button solution, yet has a wide range of features and configuration options.
- Live viewing: All recorded data can be viewed live by all stakeholders, such as test managers, students, engineers, designers, marketing managers, or other interested parties.
Human Factors Research
What is Human Factors Research?

Human factors research examines human behavior and processes, including human capabilities and limitations, to develop designs and processes that best meet human needs.
Some key questions that human factors researchers investigate:
- How can we design technologies and systems to be more user-friendly and intuitive?
- How can we improve safety and efficiency of complex systems like aviation, healthcare and transport?
- How can we design workplaces that promote wellbeing, productivity and creativity?
- How can we consider impact of new technologies like AI, automation and VR on human performance?
- How can we understand and account for effects of age, culture and individual differences?
- How can we promote effective communication and teamwork in high-stress environments?
- How can we design effective training and education programs?
- How can we evaluate effectiveness of measures to improve human performance?
In short, human factors research is about how people interact with technology, systems and environments.
Human Factors Research Testperson These issues relate to practical challenges and have an impact on improving human well-being, productivity and safety.
Research in the field of human factors can lead to practical solutions and innovations that benefit individuals, organisations and society as a whole.
Synchronizing Multiple Data Modalities
Synchronized recording of all data is the main challenge, but a full-featured Mangold Human Factors Lab makes it possible and manageable. Another often underestimated but major challenge is playing back and reviewing all collected data streams synchronously to find relevant results.
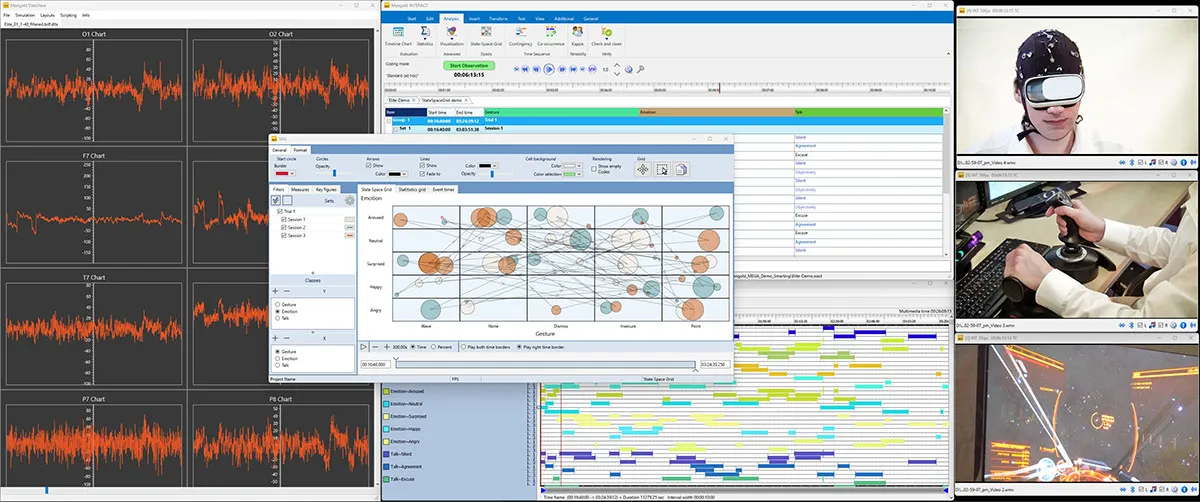
To accomplish these challenges, the Mangold Human Factors lab includes a combination of software modules, tailored to your needs:
- Mangold VideoSyncPro Studio
- Mangold INTERACT
- Mangold DataView
- Optional: Mangold Vision and Mangold LogSquare
In addition, according to your specific needs, it will include various hardware devices like cameras, bio-physiological sensors, and maybe an eye tracker. These software and hardware packages work together hand in hand to integrate different data modalities.
Integrate Multiple Data Modalities
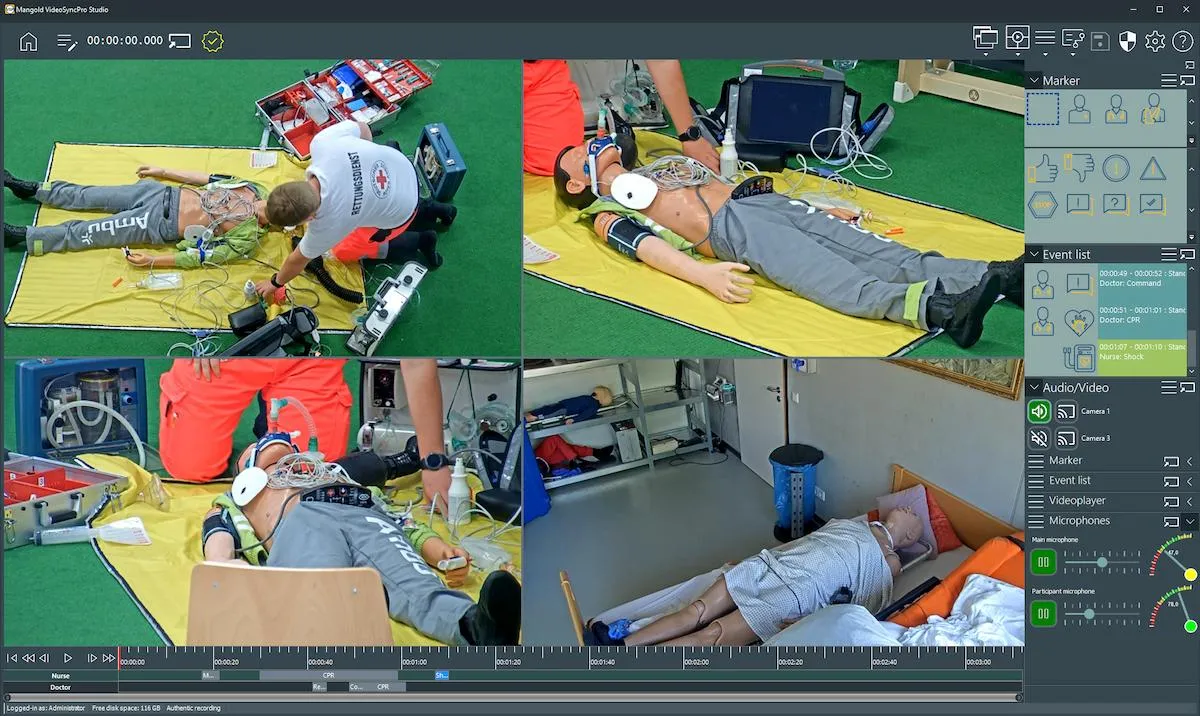

During recording, Mangold VideoSyncPro Studio is the linchpin of each Mangold Human Factors Lab.
It records multiple audio and video sources in sync, accepts markers from different sources, functions as a debriefing station, and can send a signal to third-party recorders that allow us to insert a synchronization entry.
Synchronization Between Lab Components
Mangold VideoSyncPro Studio can send a ‘recording started’ signal to external recorders in several ways: through your network via UDP, by using a USB switch in combination with a dedicated cable to the external recorder, by a keyboard signal for applications running on the same computer as VideoSyncPro Studio, or by a binary LTP port signal with a dedicated cable.
It is also possible to remotely control VideoSyncPro Studio from an external application using UDP signals. This method allows you, for example, to start recording externally if this external application can send custom UDP commands.
Lastly, activating presets to position one or more cameras automatically inserts markers into the recording log file for visual reference and identification of a change in position. External events captured from or generated by external devices or third-party software products can also be automatically inserted as markers or imported afterward.
Adding Observations to Measurements
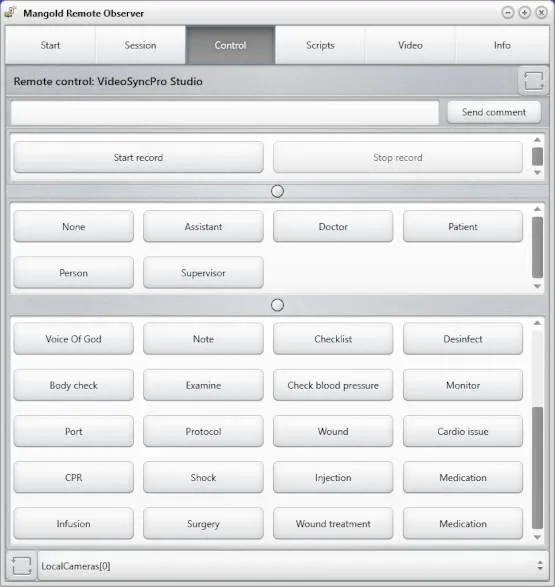
Each lab comes with Mangold Remote Observer for supervising and controlling recording sessions. Using a handheld device, you can:
- Start/stop recordings
- Log markers during sessions
- Control cameras with presets
Multiple Remote Observers can connect to the same sessions to log independent observations from another perspective or while each observer focuses on a different participant.
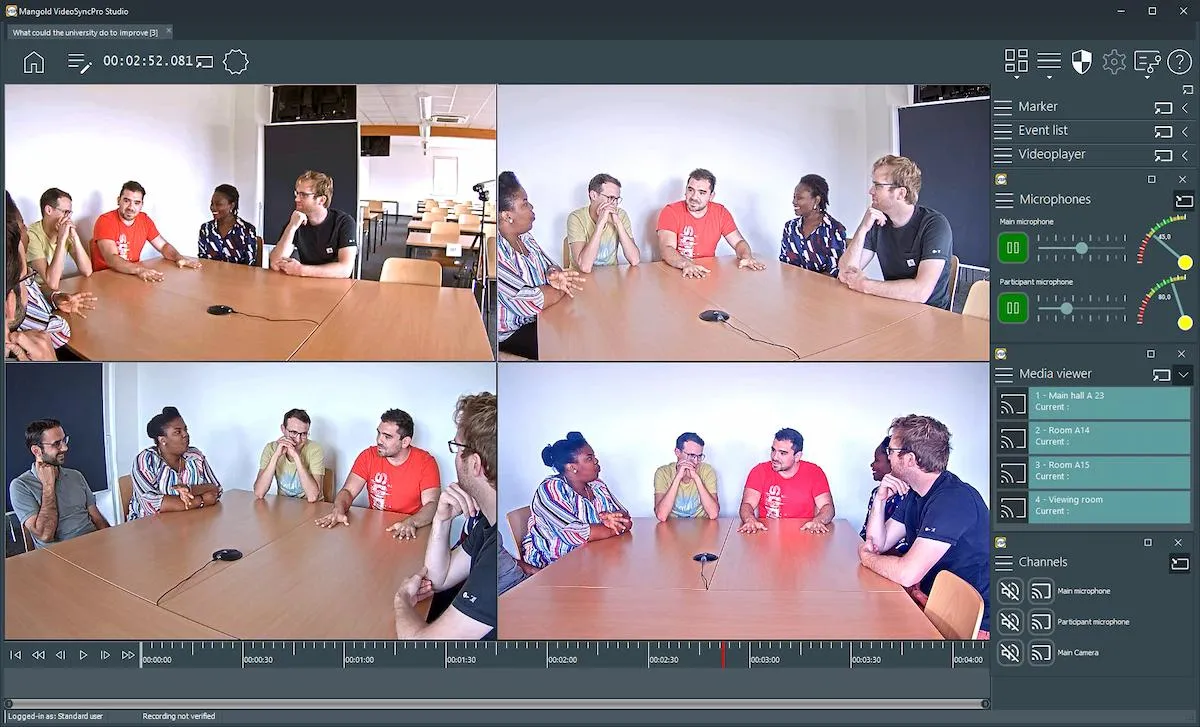
After the session, you can enrich your live observations with further details in Mangold VideoSyncPro Studio using its Marker & Debriefing functions.
Alternatively, you can transfer your live-markers to Mangold INTERACT to add fine-granulated observations with perfect timing and maybe using hierarchical Coding Systems if required. Mangold INTERACT allows you to go into much more detail and enables close examination of all sources simultaneously.
Benefits of Integrating Observations and Sensor-based Measurements
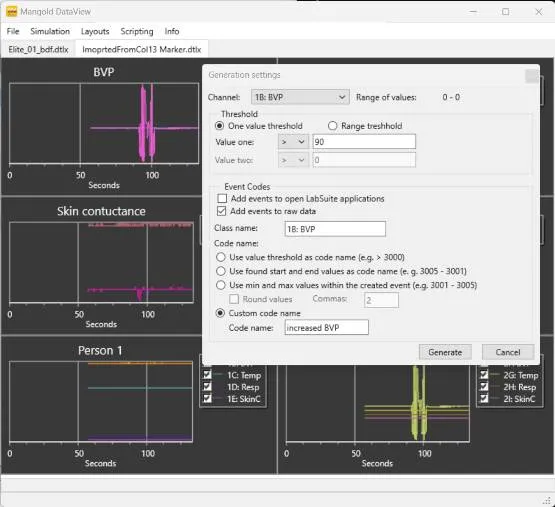
For starters, measured values can be used to automatically generate Events into Mangold INTERACT , based on values in a specific channel.
This functionality allows you to watch exactly those sequences in the video, or examine what happened in the last so many seconds before a specific drop or increase of values occurred, etc.
For example, whenever the participant’s heart rate rises above 90 bpm, you want to examine a) if there are any visual signs of this increased heart rate and b) what happened in the last, e.g. 30 seconds before this threshold was breached.
Secondly, you can quickly transfer the observation codes you used for your observations directly into the raw measured data. This function applies all selected observation codes assigned to specific time frames to all values measured during exactly these time frames.
The combination of measured values and observational data on this raw data level allows you to calculate totals, averages, standard deviations, and more over the measured values per observed behavior right away or process the combined values and observations through special statistics applications like R.
Analyzing Multidimensional Data

For a Mangold Human Factors Research lab, the software module Mangold INTERACT is the central application for multidimensional data analysis. With its external data visualization module Mangold DataView we create dynamic charts with the captured numeric data running in sync with your videos.
Combining events that were automatically generated based on measured values with manually logged observations and applying the available time-related data mining functions can really help you to get the best out of all data collected.
With Mangold INTERACT, you can, among other things, determine contingencies, find specific co-occurrences, and generate coding segments for the overlapping of all information or run the sequence analysis routine.
As discussed before, it is crucial to synchronize all your data streams for in-depth analysis. Ideally, this synchronization is covered during recording and the import process.
Still, Mangold INTERACT and its external data visualization module Mangold DataView provide several mechanisms to manually synchronize your observational data, videos, and externally recorded data values. You can adapt the required offset with millisecond accuracy for any data stream, including video.
The “Dirty Dozen” in Human Factors Research
The “Dirty Dozen” summarizes twelve common sources of human error leading to safety incidents. Originally developed for aviation by Gordon Dupont, it’s now used across industries for safety training:
- Lack of communication: Lack of or unclear communication can lead to misunderstandings and critical information being lost, jeopardising safety.
- Fatigue: Fatigue reduces concentration and judgement, which increases the likelihood of errors.
- Lack of teamwork: Poor teamwork can lead to inefficient work processes and misunderstandings that jeopardise safety.
- Distraction: Unforeseen disruptions or interruptions can take focus away from important tasks, which can lead to errors.
- Lack of resources: Lack of or insufficient resources, such as tools, time or personnel, can lead to improvised solutions and potentially unsafe working practices.
- Pressure: Time or performance pressure can lead to decisions being made hastily, increasing the likelihood of errors.
- Complacency: Overconfidence in one’s own abilities or in best practice can lead to underestimating risks and ignoring safety precautions.
- Lack of reassurance: Failure to verify important information or actions can lead to errors going undetected and escalating.
- Poor ergonomics: Inappropriate working conditions or equipment can lead to physical stress, errors and injuries.
- Lack of knowledge: Insufficient knowledge or training about procedures, equipment or situations can lead to employees making unsafe decisions.
- Lack of attention: When people rely on routine tasks, vigilance can wane, causing signs of problems to be missed.
- Standards: Informal pressure to accept ways of working that do not conform to prescribed procedures can lead to unsafe practices and ultimately incidents.
Why are the “Dirty Dozen” important?
The “Dirty Dozen” help to raise awareness of human factors that can affect safety in different working environments. They serve as a checklist and training tool to identify and minimise risks and promote a strong safety culture. By understanding and addressing these twelve hazards, we can prevent accidents and make the working environment safer.
Human Factors Research Lab and Multimodal Data
In order to answer these complex questions, a lot of different data needs to be collected.
Measuring the various signals from the human body in response to the different stimuli from our environment is one part of this data, observing the participants during their daily work is another part.
Sometimes signals from devices we interact with, such as computers, gaze data, simulation stations, etc., are also included in the data pool.
By measuring and integrating these physiological signals in combination with real-life observations, we can better understand conscious and unconscious reactions.
Typical modalities that may be of interest for a human research study are:
- Recorded videos
- Screen recordings that are recorded synchronously with other cameras
- Markers and notes collected during the recording
- Behavioral events recorded by a human observer
- Physiological signals recorded by third-party data collection systems
- Gaze data from eye trackers
- Data from other programmes that can provide text files with time information or a fixed sampling rate
- Keystrokes, mouse clicks and other events recorded by Mangold LogSquare, for example
- Facial expressions, recorded manually or recognised automatically by an AI
- Audio data from microphones
- Data from other devices that can provide time-synchronized data, such as heart rate monitors or accelerometers
The time-synchronized integration of the various collected data is essential for a comprehensive understanding of these processes in their different contexts.
For this reason, a Mangold Human Factors Research Lab usually contains various devices for recording video and audio signals, bio-psychological measurements, EEG data, eye-tracking data and stimulus generators.
UX and Usability Research
What is User Experience and Usability?
User experience (UX) and usability are concerned with designing and optimising the interaction between people and digital products in order to ensure a positive, intuitive and efficient user experience.
Usability focuses on functionality and user-friendliness - in other words, how easy and efficient a product is to use.
User experience (UX), on the other hand, looks at the entire user experience, including usability, but also other factors such as emotions, expectations and overall satisfaction.
While usability is a part of user experience, user experience is the broader term that includes functionality as well as the emotional and aesthetic aspects of user interaction with a product.

Key research questions include:
- How can we design digital products and systems to be more intuitive and user-friendly?
- How can we improve user satisfaction and efficiency when interacting with complex systems such as websites, mobile applications and software solutions?
- How can we design digital work environments that promote well-being, productivity and creativity?
- How can we consider the impact of new technologies such as artificial intelligence, automation and augmented reality on user behavior and experience?
- How can we better understand the different needs and expectations of users from different backgrounds, cultures and age groups and incorporate them into design processes?
- How can we develop effective communication strategies and user interfaces in environments with high workloads and stress?
- How can we design training and learning programs that are efficient, engaging and user-centric?
- How can we evaluate and measure the effectiveness of measures and technologies to improve user experience and usability?
In short, UX and usability is about how users interact with digital products and systems and how these interactions can be optimised.
Why is UX and usability important?
These questions address real-world challenges and have a significant impact on improving user satisfaction, productivity and efficiency in the digital world. Research in UX and usability can lead to innovative solutions that benefit not only users, but also companies and society as a whole.
UX and usability lab: collecting and analysing user data
In order to answer these complex questions, various data modalities are collected and analysed. These include physiological signals, eye-tracking data, mouse movements, click behavior and qualitative feedback from users.

Successful Products Through Usability
Successful companies have one thing in common: their products are highly valued by customers. And why? Most often, the key factor is user-friendliness, in other words, usability.
Whether it is websites, software programs, smartphones or machines – when products and services are developed it should always be about the people who use them.
Instead many a developer of machines or programs get lost in their love of technology and perform function overkill
But: most products don’t even use their full potential. They play a subordinate role and aren’t even the decisive factor for success on the market.
The key factor and unique selling point in competition is rather the intuitive handling – the usability.
Success factor usability with Mangold LogSquare Thus user- friendly is a decisive factor for a product’s success. To reach this added value, the development and implementation of a product should be the primary aim.
Because: User-friendly products can be the reason for a winning difference, plus these products are gaining more importance. The reason being, that users weigh the importance of usability as a purchase criteria. The same applies to the end-user, as well as for B2B relationships. Suppliers who integrate usability in their products achieve a higher customer satisfaction and for that reason are especially successful in the market.
User-friendly products reduce the learning time, minimize operating errors, increase the work production and escalate the working process.
A high usability supports the user in completing his tasks quickly, accurately, and to his satisfaction which helps in making it possible to reach goals intuitively.
Contact Us

Mangold International offers specialized solutions for usability and UX labs based on years of experience. Our solutions serve:
- Universities
- Service companies
- Financial providers
- Travel companies
- Game developers
- Web portals
- Hospitality businesses
- Industrial companies
Let us help find your ideal lab solution for conducting observational studies and understanding customer perspectives.
Mangold Observation Labs
Mangold Observation Labs is a comprehensive turn-key solution for conducting behavioral research and observation.
